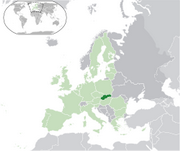
| 1 | January | Czechoslovakia split into the Czech Republic and Slovakia in 1993. |
| 6 | January | Epiphany (from Koine Greek (ἡ) ἐπιφάνεια, epiphaneia "appearance", "manifestation") is a Christian feast day that celebrates the revelation of God made Man in the person of Jesus Christ. It falls on 6 January or, in many countries, on the Sunday that falls between 2 January and 8 January. Since the Julian Calendar, which is followed by some Eastern Churches, is at present 13 days behind the Gregorian Calendar and the revised Julian Calendar, 6 January in that calendar corresponds at present to 19 January in what is the official civil calendar in most countries. On this feast, Western Christians commemorate principally the visitation of the Biblical Magi to the Baby Jesus, i.e., his manifestation to the Gentiles; Eastern Christians commemorate the baptism of Jesus in the Jordan River, seen as his manifestation to the world as the Son of God. It is also called Theophany, especially by Eastern Christians. |
| 3 | April | Good Friday, also called Holy Friday, Black Friday, or Great Friday, is a holiday observed primarily by adherents to Christianity commemorating the crucifixion of Jesus and his death at Calvary. The holiday is observed during Holy Week as part of the Paschal Triduum on the Friday preceding Easter Sunday, and often coincides with the Jewish observance of Passover.
Based on the scriptural details of the Sanhedrin Trial of Jesus, the Crucifixion of Jesus was most probably on a Friday. The estimated year of Good Friday is AD 33, by two different groups, and originally as AD 34 by Isaac Newton via the differences between the Biblical and Julian calendars and the crescent of the moon. A third method, using a completely different astronomical approach based on a lunar Crucifixion darkness and eclipse model (consistent with Apostle Peter's reference to a "moon of blood" in Acts 2:20) arrives at the same date, namely Friday April 3, AD 33. |
| 6 | April | Easter (Greek: Πάσχα) is the most important annual religious feast in the Christian liturgical year. According to Christian scripture, Jesus was resurrected from the dead on the third day of his crucifixion. Christians celebrate this resurrection on Easter Day or Easter Sunday (also Resurrection Day or Resurrection Sunday), two days after Good Friday and three days after Maundy Thursday. The chronology of his death and resurrection is variously interpreted to be between AD 26 and AD 36. Easter also refers to the season of the church year called Eastertide or the Easter Season. Traditionally the Easter Season lasted for the forty days from Easter Day until Ascension Day but now officially lasts for the fifty days until Pentecost. The first week of the Easter Season is known as Easter Week or the Octave of Easter. Easter also marks the end of Lent, a season of fasting, prayer, and penance.
Easter is a moveable feast, meaning it is not fixed in relation to the civil calendar. The First Council of Nicaea (325) established the date of Easter as the first Sunday after the full moon (the Paschal Full Moon) following the vernal equinox. Ecclesiastically, the equinox is reckoned to be on March 21. The date of Easter therefore varies between March 22 and April 25. Eastern Christianity bases its calculations on the Julian Calendar whose March 21 corresponds, during the twenty-first century, to April 3 in the Gregorian Calendar, in which calendar their celebration of Easter therefore varies between April 4 and May 8.
Easter is linked to the Jewish Passover not only for much of its symbolism but also for its position in the calendar.
Relatively newer elements such as the Easter Bunny and Easter egg hunts have become part of the holiday's modern celebrations, and those aspects are often celebrated by many Christians and non-Christians alike. |
| 1 | May | International Workers' Day (a name used interchangeably with may day) is a celebration of the social and economic achievements of the international labor movement. May Day commonly sees organized street demonstrations and street marches by millions of working people and their labour unions throughout most of the countries of the world. |
| 8 | May | Victory Day (Deň víťazstva nad fašizmom) |
| 5 | July | Saints Cyril and Methodius (Greek: Κύριλλος καὶ Μεθόδιος, Old Church Slavonic: Кѷриллъ и Меѳодїи[more]) were two Byzantine Greek brothers born in Thessaloniki in the 9th century. They became missionaries of Christianity among the Slavic peoples of Great Moravia and Pannonia. Through their work they influenced the cultural development of all Slavs, for which they received the title "Apostles to the Slavs". They are credited with devising the Glagolitic alphabet, the first alphabet used to transcribe the Old Church Slavonic language. After their deaths, their pupils continued their missionary work among other Slavs. Both brothers are venerated in the Eastern Orthodox Church as saints with the title of "Equals to the Apostles". In 1880, Pope Leo XIII introduced their feast into the calendar of the Roman Catholic Church. In 1980, Pope John Paul II declared them co-patrons of Europe, together with Saint Benedict of Nursia. |
| 29 | August | The Slovak National Uprising (Slovak: Slovenské národné povstanie, abbreviated SNP) or 1944 Uprising was an armed insurrection organized by the Slovak resistance movement during World War II. It was launched on August 29 1944 from Banská Bystrica in an attempt to overthrow the collaborationist Slovak State of Jozef Tiso. Although the rebel forces were defeated by Nazi Germany, guerrilla warfare continued until the Soviet Army occupied Slovakia in 1945. |
| 1 | September | 1992 - The constitution of (future) independent Slovakia has been adopted in Bratislava. |
| 15 | September | Our Lady of Sorrows (Latin: Beata Maria Virgo Perdolens), the Sorrowful Mother or Mother of Sorrows (Latin: Mater Dolorosa, at times just Dolorosa), and Our Lady of the Seven Sorrows or Our Lady of the Seven Dolours are names by which the Blessed Virgin Mary is referred to in relation to sorrows in her life. As "Mater Dolorosa", it is also a key subject for Marian art in the Catholic Church. Our Lady of Sorrows is the patron saint of Slovakia. |
| 1 | November | All Saints' Day (in the Catholic Church officially the Solemnity of All Saints and also called All Hallows or Hallowmas), often shortened to All Saints, is a solemnity celebrated on 1 November in Western Christianity, and on the first Sunday after Pentecost in Eastern Christianity, in honour of all the saints, known and unknown.
In terms of Western Christian theology, the day commemorates all those who have attained the beatific vision in Heaven. In the Roman Catholic Church, the next day, All Souls' Day, specifically commemorates the departed faithful who have not yet been purified and reached heaven. It is a national holiday in many historically Catholic countries. |
| 17 | November | Commemorating the student demonstration against Nazi occupation in 1939, and especially the demonstration in 1989 in Prague considered to mark the beginning of the Velvet Revolution. |
| 24 | December | Christmas Eve is the day before Christmas Day, a widely celebrated holiday commemorating the birth of Jesus of Nazareth. It is a culturally significant celebration for most of the Western world and is widely observed as a full or partial holiday in anticipation of Christmas.
In Western culture, Christmas Eve is celebrated on December 24. However, the Coptic, Serbian, Russian, Macedonian, and Georgian Orthodox Churches, as well as the Greek Orthodox Church of Jerusalem, use the Julian calendar, which is currently thirteen days behind the Gregorian calendar, so Christmas Eve for the adherents of those Churches coincides with January 6 of the following year in the Gregorian calendar. |
| 25 | December | Christmas or Christmas Day is an annual Christian holiday commemorating the birth of Jesus Christ. It is celebrated on December 25, but this date is not known to be Jesus' actual birthday, and may have initially been chosen to correspond with either the day exactly nine months after some early Christians believed Jesus had been conceived, a historical Roman festival, or the date of the northern hemisphere's winter solstice. Christmas is central to the Christmas and holiday season, and in Christianity marks the beginning of the larger season of Christmastide, which lasts twelve days |
| 26 | December | Boxing Day is a bank and public holiday commonly occurring on the 26th of December. It is observed in the United Kingdom, Australia, Canada, Ghana, Switzerland, Germany, Greenland, Netherlands, New Zealand, Hong Kong, Nigeria,Kenya, Guyana, Trinidad & Tobago, Jamaica and countries in the Commonwealth of Nations with a mainly Christian population. In South Africa this public holiday is now known as the Day of Goodwill. Though it is not an official holiday in the United States, the term "Boxing Day" is used by some Americans, particularly those that live near the Canada – United States border. In Canada, Boxing Day is listed in the Canada Labour Code as a holiday. It is not an official holiday in Quebec or British Columbia.
The traditional recorded celebration of Boxing Day has long included giving money and other gifts to those who were needy and in service positions. The European tradition has been dated to the Middle Ages, but the exact origin is unknown and there are some claims that it goes back to the late Roman/early Christian era; metal boxes were placed outside churches used to collect special offerings tied to the Feast of Saint Stephen. In the United Kingdom it certainly became a custom of the nineteenth century Victorians for tradesmen to collect their "Christmas boxes" or gifts in return for good and reliable service throughout the year on the day after Christmas. However, the exact etymology of the term "Boxing" is unclear, with several competing theories, none of which is definitively true. Another possibility is that the name derives from an old English tradition: in exchange for ensuring that wealthy landowners' Christmases ran smoothly, their servants were allowed to take the 26th off to visit their families. The employers gave each servant a box containing gifts and bonuses (and sometimes leftover food). In addition, around the 1800s, churches opened their alms boxes (boxes where people place monetary donations) and distributed the contents to the poor. |


 Po polsku
Po polsku
 Auf Deutsch
Auf Deutsch
 En Française
En Française
 En Español
En Español
 На Русском
На Русском
 在中國
在中國